System Description¶
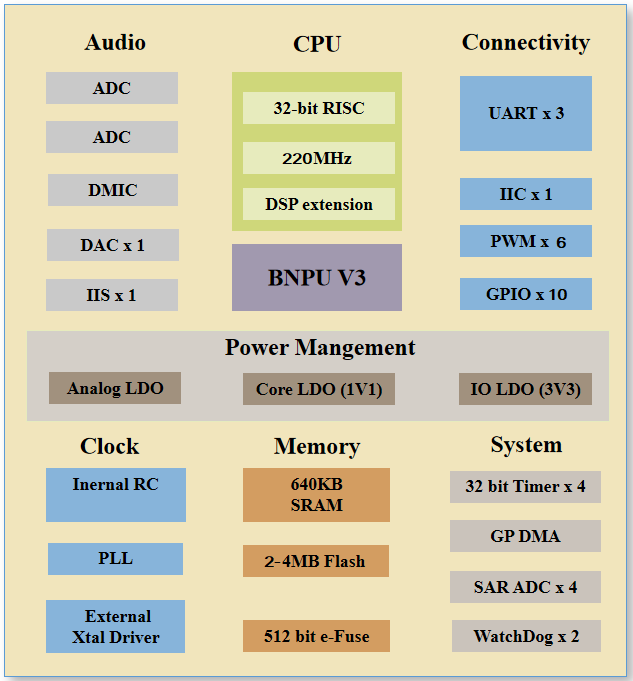
The block diagram of the chip system is shown in Figure S-1. It is composed of multiple modules, including brain neural network processor BNPU, etc. The functional interfaces of CI1301, CI1302 and CI1303 chips are identical, only the size of the built-in Flash is different. CI1301 is 1MB, CI1302 is 2MB, and CI1303 is 4MB. Each module is described below.
System architecture¶
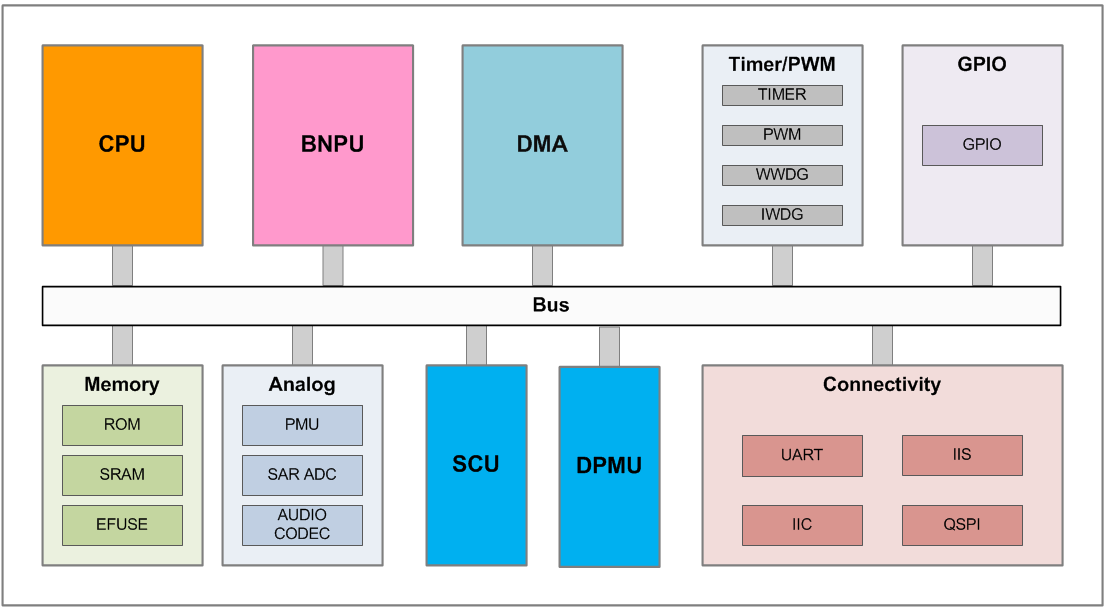
The chip system includes BNPU, CPU, ROM, SRAM, DMA and various peripheral interfaces. Each functional module communicates and controls through the bus supporting multi-core parallel processing architecture, and its architecture is shown in Figure S-2.
Register Mapping¶
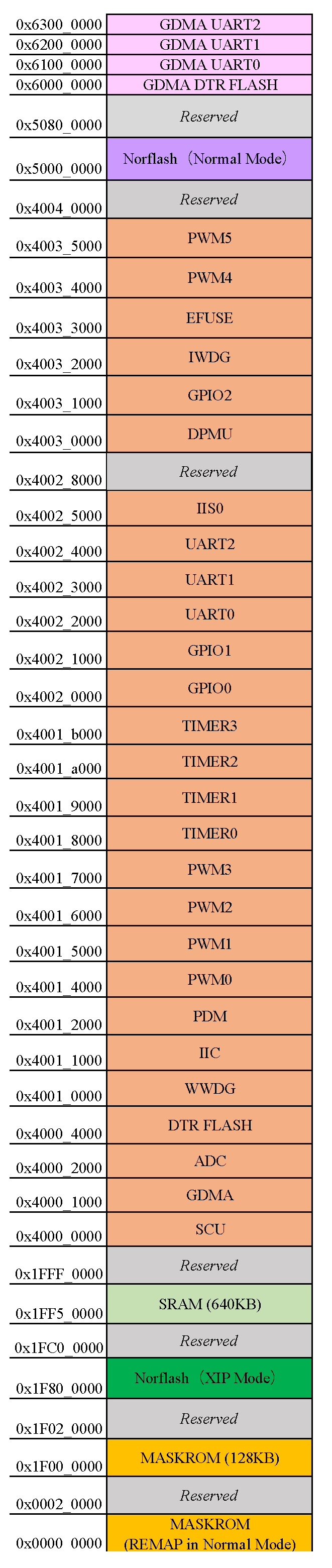
The chip register mapping is shown in Figure S-3, and the internal ROM start address starts from 0x00000000; The starting address of SRAM starts from 0x1FF00000 to 0x1FF7FFFF, totaling 640Kbytes. The rest are the starting addresses of the peripheral interfaces.
Interrupt¶
The chip integrates a kernel interrupt controller, which can process interrupts efficiently. The functions of the controller are described as follows:
- Support software interrupt, timer interrupt and external interrupt;
- 32 programmable external interrupts;
- 3 bits interrupt priority configuration, that is, 8 priority levels;
- Support the software to dynamically and programmatically modify the interrupt level and interrupt priority values;
- Support interrupt nesting based on interrupt level;
- Support fast vector interrupt processing mechanism;
- Support quick tail biting mechanism;
- NMI (Non Maskable Interrupt) is supported.
The interrupt vector table is shown in the following table. After the corresponding interrupt occurs, the CPU will execute instructions from the corresponding interrupt entry address.
| IRQ No. | Interrupt Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | INT_ WWDG | Window watchdog interrupt |
| 1 | INT_ SCU | SCU interrupt |
| 2 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 3 | INT_ ADC | ADC controller interrupt |
| 4 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 5 | INT_ TIMER0 | Timer 0 interrupt |
| 6 | INT_ TIMER1 | Timer 1 interrupt |
| 7 | INT_ TIMER2 | Timer 2 interrupt |
| 8 | INT_ TIMER3 | Timer 3 interrupt |
| 9 | INT_ IIC | IIC interrupt |
| 10 | INT_ GPIO0 | GPIO0 interrupt |
| 11 | INT_ GPIO1 | GPIO1 interrupt |
| 12 | INT_ UART0 | UART0 interrupt |
| 13 | INT_ UART1 | UART1 interrupt |
| 14 | INT_ UART2 | UART2 interrupt |
| 15 | INT_ IIS0 | IIS0 interrupt |
| 16 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 17 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 18 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 19 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 20 | INT_ PDM | PDM interrupt |
| 21 | INT_ DTR | DTR Flash controller interrupt |
| 22 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 23 | INT_ VDT | Low voltage detection indication interrupt |
| 24 | INT_ EXT0 | External interrupt 0 |
| 25 | INT_ EXT1 | External interrupt 1 |
| 26 | INT_ IWDG | Independent watchdog interrupt |
| 27 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 28 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 29 | INT_ EFUSE | EFUSE controller interrupt |
| 30 | INT_ GPIO2 | GPIO2 interrupt |
Module Overview¶
This document will describe in detail the modules and registers frequently used by users, as follows:
-
System control unit SCU
-
DMA
- Universal timer and PWM output
- Independent watchdog (IWTD)
- Window Watchdog (WWTD)
- DTR_ FLASH
- IIC
- IIS
- UART
- GPIO
- ADC
- EFUSE
The configuration and use of other modules, such as BNPU, CODEC, PDM, power management and PLL, EFUSE, have been included in the basic components provided by the CI130X SDK. It is not recommended that users directly modify the driver or directly operate the register to avoid abnormal operation of the basic components. It is recommended to directly use the standard driver interface provided in the CI130X SDK. If you really have special needs, please contact our technical support personnel for support.